What is JAX?
JAX is a high-performance accelerator-oriented array computing library for Python developed by Google. It allows composition, JIT-compilation, transformation, and automatic differentiation of numerical programs.
It provides NumPy-like and lower-level APIs.
It also requires strict functional programming.
Why JAX?
Fast
Default data type suited for deep learning
Like PyTorch , uses float32 as default. This level of precision is suitable for deep learning and increases efficiency (by contrast, NumPy defaults to float64).
JIT compilation
The same code can run on CPUs or on accelerators (GPUs and TPUs )
XLA (Accelerated Linear Algebra) optimization
Asynchronous dispatch
Vectorization, data parallelism, and sharding
All levels of shared and distributed memory parallelism are supported.
Great AD
01
Autodiff method
1
Static graph
and XLA
02
Framework
2
Dynamic graph
1->2
a
TensorFlow
4
Dynamic graph
and XLA
2->4
b
PyTorch
5
Pseudo-dynamic
and XLA
4->5
d
TensorFlow2
e
JAX
03
Advantage
7
Mostly
optimized AD
8
Convenient
9
Convenient
10
Convenient and
mostly optimized AD
04
Disadvantage
A
Manual writing of IR
B
Limited AD optimization
D
Disappointing speed
E
Pure functions only
(subset of Python)
summarized from a blog post by Chris Rackauckas
Close to the math
Considering the function f:
= lambda x: x** 3 + 2 * x** 2 - 3 * x + 8 We can create a new function dfdx that computes the gradient of f w.r.t. x:
from jax import grad= grad(f)dfdx returns the derivatives:
4.0
Forward and reverse modes
reverse-mode vector-Jacobian products: jax.vjp
forward-mode Jacobian-vector products: jax.jvp
Higher-order differentiation
With a single variable, the grad function calls can be nested:
= grad(dfdx) # function to compute 2nd order derivatives = grad(d2fdx) # function to compute 3rd order derivatives With several variables, you have to use the functions:
jax.jacfwd for forward-mode,jax.jacrev for reverse-mode.
How does it work?
tracer
Tracing
jaxpr
Jaxprs
(JAX expressions)
intermediate
representation
(IR)
tracer->jaxpr
jit
Transformation
hlo
High-level
optimized (HLO)
program
jit->hlo
xla
Accelerated
Linear Algebra
(XLA)
CPU
CPU
xla->CPU
GPU
GPU
xla->GPU
TPU
TPU
xla->TPU
transform
Transformations
py
Pure Python
functions
py->tracer
jaxpr->jit
jaxpr->transform
hlo->xla
tracer
Tracing
jaxpr
Jaxprs
(JAX expressions)
intermediate
representation
(IR)
tracer->jaxpr
jit
Just-in-time
(JIT)
compilation
hlo
High-level
optimized (HLO)
program
jit->hlo
xla
Accelerated
Linear Algebra
(XLA)
CPU
CPU
xla->CPU
GPU
GPU
xla->GPU
TPU
TPU
xla->TPU
transform
Vectorization
Parallelization
Differentiation
py
Pure Python
functions
py->tracer
jaxpr->jit
jaxpr->transform
hlo->xla
tracer
Tracing
jaxpr
Jaxprs
(JAX expressions)
intermediate
representation
(IR)
tracer->jaxpr
jit
jax.jit
hlo
High-level
optimized (HLO)
program
jit->hlo
xla
Accelerated
Linear Algebra
(XLA)
CPU
CPU
xla->CPU
GPU
GPU
xla->GPU
TPU
TPU
xla->TPU
transform
jax.vmap
jax.pmap
jax.grad
py
Pure Python
functions
py->tracer
jaxpr->jit
jaxpr->transform
hlo->xla
JAX for AI
Not itself a DL library
jx
JAX
dl
Deep learning
jx->dl
op
Optimizers
jx->op
pp
Probabilistic
programming
jx->pp
pm
Probabilistic
modeling
jx->pm
ll
LLMs
ll->jx
so
Solvers
so->jx
ph
Physics
simulations
ph->jx
A sublanguage ideal for DL
jx
JAX
dl
Deep learning
jx->dl
op
Optimizers
jx->op
pp
Probabilistic
programming
jx->pp
pm
Probabilistic
modeling
jx->pm
ll
LLMs
ll->jx
so
Solvers
so->jx
ph
Physics
simulations
ph->jx
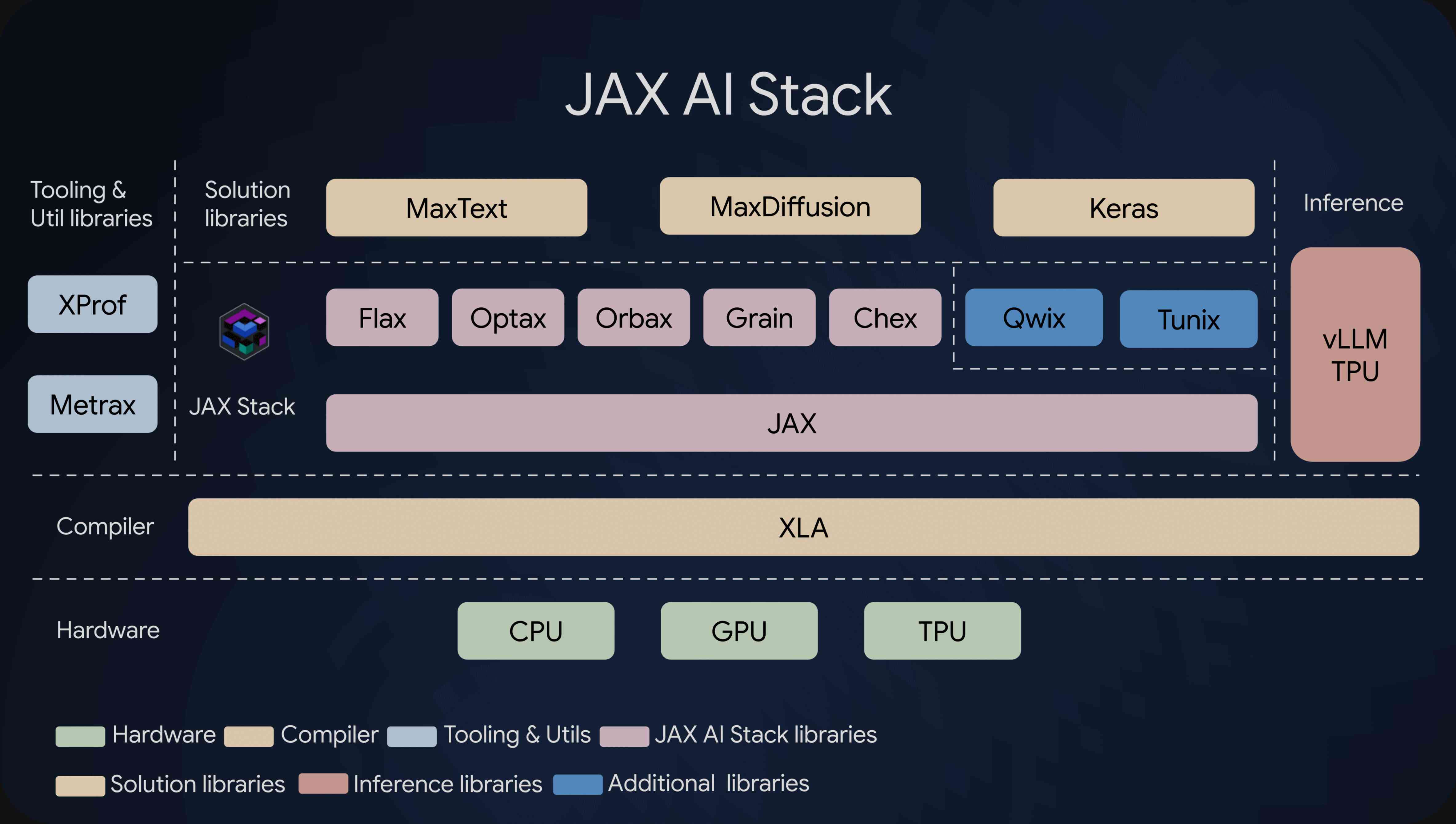
The JAX AI stack
A modular approach: