Introduction
What is scikit-learn and how does it fit in the wide landscape of machine learning frameworks?
What is machine learning?
Maybe we should start with some definitions:
Artificial intelligence (AI) can be defined as any human-made system mimicking animal intelligence. This is a large and very diverse field.
Machine learning (ML) is a subfield of AI that can be defined as computer programs whose performance at a task improves with experience. This learning can be split into three categories:
Supervised learning
Regression is a form of supervised learning with continuous outputs.
Classification is supervised learning with discrete outputs.Supervised learning uses training data in the form of example input/output pairs.
The goal is to find the relationship between inputs and outputs.
Unsupervised learning
Clustering, social network analysis, market segmentation, dimensionality reduction (e.g. PCA), anomaly detection … are all forms of unsupervised learning.
Unsupervised learning uses unlabelled data and the goal is to find patterns within the data.
Reinforcement learning
The algorithm explores by performing random actions and these actions are rewarded or punished (bonus points or penalties).
This is how algorithms learn to play games.
Deep learning (DL) is itself a subfield of machine learning using deep artificial neural networks.
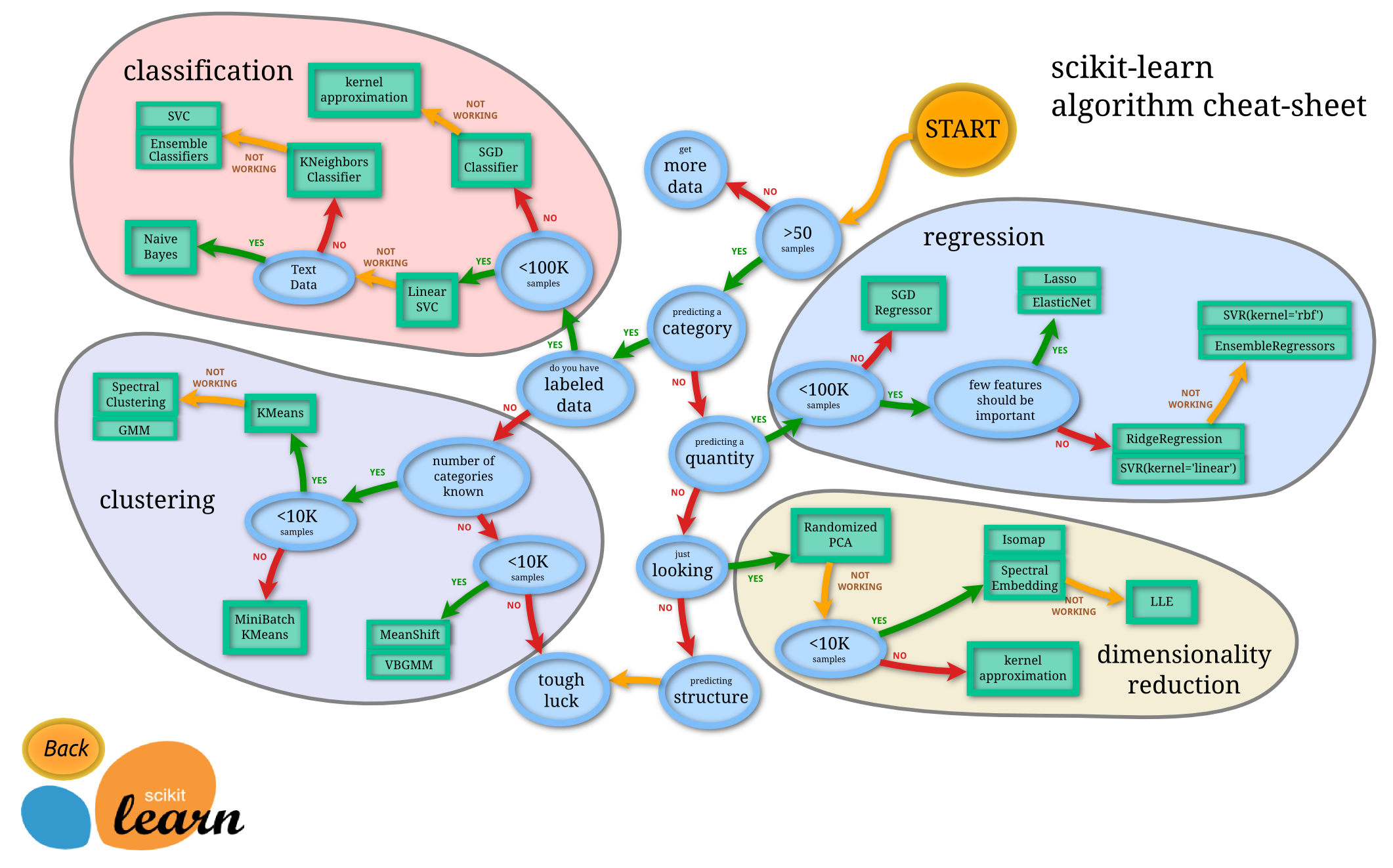
What is scikit-learn?
Scikit-learn (also called sklearn) is a free and open source set of libraries for Python built on top of SciPy (thus using NumPy’s ndarray as the main data structure) used for machine learning.
Sklearn is a rich toolkit characterized by a clean, consistent, and very simple API.
It is easy to learn and very well documented. You can think of it as a vast collection of routines that are easy to apply and require little computing power.
Scikit-learn in the ML landscape
There are many machine learning frameworks. While sklearn has many advantages (ease of use, wide range of tools), it has clear limitations: there is no GPU support and deep learning and reinforcement learning are out of its scope (the only neural network implemented is a multilayer perceptron (an historical, very basic, and terribly inefficient neural network).
If you want to access the power and flexibility that deep neural networks provide, you should turn towards tools such as PyTorch (wonderful tool both in academia, research, and industry) or the higher-level Keras (easy API, easy to learn, but less flexible).